Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding (AUB)
Disorders of menstrual bleeding, now termed AUB. Abnormal uterine bleeding (AUB) is bleeding from the uterus that is longer than usual or that occurs at an irregular time. Bleeding may be heavier or lighter than usual and occur often or randomly. AUB can occur: As spotting or bleeding between your periods. Although rarely life threatening, menstrual disorders can cause major social, psychological and occupational upset.
Types of abnormal bleeding:
There are
several types of abnormal bleeding and their terminology should be known;
1. Heavy menstrual bleeding (HMB)
2. Intermenstrual bleeding (IMB)
3. Postcoital bleeding (PCB)
4. Postmenopausal bleeding (PMB)
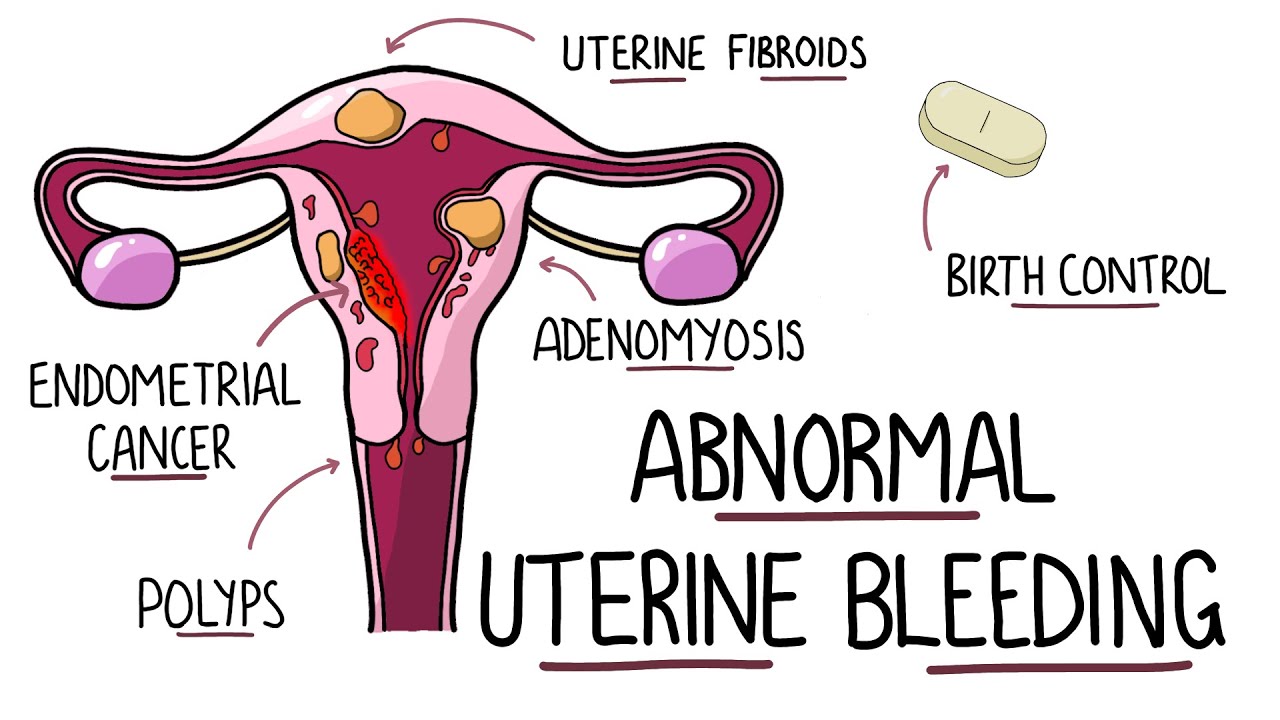
Causes of abnormal uterine bleeding
The most
common causes of such bleeding are uterine
fibroids, uterine adenomyosis,
or endometrial polyps. Fibroids are
benign masses in the muscle layer of the uterus (myometrium), while adenomyosis
is a condition in which the lining of the uterus (endometrium) grows into the
myometrium.
1. Heavy menstrual bleeding (formerly
called menorrhagia).
2. Bleeding at unusual times (between
periods, after intercourse).
3. Unusually long periods (seven days or
longer).
4. Inconsistent menstrual cycles.
Investigation of abnormal uterine bleeding
1. Initial investigations for each include;
2. Speculum examination of the cervix,
with swabs for microbiology
3. Cervical smear if indicated
4. Transvaginal ultrasound scan (TVUSS)
5. Endometrial biopsy (EB) as necessary.
6. Further to this, outpatient
·
hysteroscopy
· biopsy
Treatment of abnormal uterine bleeding
Dysfunctional uterine bleeding can be treated;
·
Medically
·
Surgically
Medical treatment:
It consists of
anti-fibrinolytic tranexamic acid, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, the
combined contraception pill, progestogen, danazol, or analogues of
gonadotrophin releasing hormone.
Surgical treatment:
It include dilation and curettage (D&C), endometrial
ablation, uterine artery embolization, and hysterectomy. The choice of
surgical modality (eg, D&C versus hysterectomy) is based on the
aforementioned factors plus the patient's desire for future fertility.
Terminologies for common types of AUB
• HMB:
Excessive
menstrual blood loss (this chapter).
• IMB:
Bleeding between periods, often seen with
endometrial and cervical polyps .
• PCB:
Bleeding
after sex. Often associated with cervical abnormalities.
• PMB:
Bleeding more than 1 year after cessation of periods. Exclude endometrial pathology or vaginal atrophy.
• BEO:
‘Bleeding of
endometrial origin’, a diagnosis of exclusion, has replaced the term ‘dysfunctional
uterine bleeding’ (DUB).
Comments
Post a Comment